EJB TRAINING
"Innovate. Integrate. Inspire The Future with SoftCrayons"
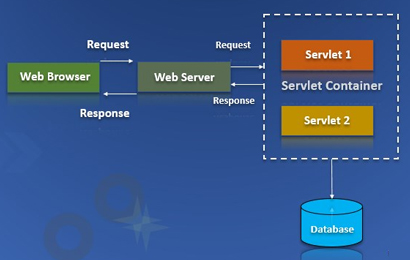
Enterprise Java Beans (EJB) is one of several Java APIs used to manufacture standard software versions for the enterprise.
EJB is an element of software that runs on servers and describes the business logic for an application.
Enterprise Java Beans web repository provides a runtime domain for web-related software components, including:
Learn, Build Skills, Grow Limitlessly. Your IT Career Starts Here.

Course Duration
1 - 3

New Batch
As per schedule hybrid mode

Payment
Flexible One-Time/Installment

Mode
Flexible Offline/Online
Professional Skill Development
Service Details
Best Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) Training Course
Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) is an important part of Java EE that lets you build fast, safe, and scalable business apps. Softcrayons offers the best EJB Certification Training in Ghaziabad. It is meant to help students and professionals learn how to write business logic on the server side.EJB handles important system-level tasks like security, transaction management, lifecycle management, and scalability, which makes it easier to design enterprise applications. The goal of our EJB training program is to help you use what you've learned in the real world with modern application servers and industry best practices.We offer training in person and online, and it's taught by experienced Java professionals who have worked on real-world projects.
What the Course Is About:
The main things we want to teach you in our EJB Certification Training are:
- To get a solid start in corporate Java development
- To help students learn how to write business logic on the server side
- To make it easier to use EJB to build business apps
- To help students get ready for jobs in enterprise Java
- To give them real-world experience with real-world problems
- We want to give students the tools they need to confidently make and use business apps.
Why Would You Want to Work with EJB?
EJB is still an important part of enterprise Java ecosystems because
- There is a lot of demand for apps for big businesses.
- Built-in help for transactions, safety, and growth
- Easier to develop business logic
- A solid foundation for Java EE and enterprise frameworks
- Used in telecommunications, banking, healthcare, and large IT systems
- If you know how to use EJB, you can get jobs as a Java developer at big companies.
How much money freshmen can expect to make:
New hires who know EJB and Java EE can expect to make between INR 5 LPA and INR 6 LPA on average. People who are more experienced and know more advanced Java can make a lot more money.
Training Certificate:
Softcrayons gives students who finish the course an EJB Certification that is recognized all over the world. This certificate shows that you know how to use enterprise Java and makes you a better candidate for jobs.
Mock Interviews:
We help students get ready for real job interviews by doing practice interviews with them. The goal of these workshops is to help you improve your technical skills, problem-solving skills, and confidence in your ability to talk to people.
What makes Softcrayons the best place to learn EJB?
- Certified Java trainers with a lot of experience
- An EJB curriculum that works in the real world
- Business-level labs and projects
- Options for training in person and online
- Always help with finding a job
- Modern infrastructure and help with school
- Students give it great reviews and ratings.
Related courses:
- Best Advanced Java Training
- Best Spring and Spring Boot Training
- Best Python Full Stack
Training Features
Live Interactive Classes
Real-time doubt clearing with expert instructors
Hands-on Projects
Build portfolio with industry-standard projects
Industry Curriculum
Updated syllabus matching current job requirements
Latest Technologies
Learn cutting-edge tools and frameworks
Online & Offline
Flexible learning modes to suit your schedule
Certification Support
Prepare for global IT certifications
LEARNING PATH
Master the Syllabus
Program Highlights

Top Faculty with Certification Facility
Learn from the best, as we impart world-class education with faculty who have rich academic & industry experience
Career Service: Job Readiness
Pursuing your desire to being job-ready through resume building sessions & MasterClass for interview preparation

Choose the way you want to learn
Enhance your learning potential by your choice of printed books, audio books, e-books, videos, and live classrooms

Placement Guarantee
Benefit from our network of over 500+ hiring partners from diverse domains to ensure a smooth job transition after 1 year
Common Questions
Join Our EJB Training`
Guranteed Job Placement Program
- Expert-led training
- Hands-on projects
- Globally recognized certification
Training Certification
🎓 Earn Your Certificate
Successfully complete the training and assessments to receive your official certification. This credential validates your skills and enhances your career opportunities.
Showcase your achievements and share your milestones with your network to inspire others and grow your professional connections.

Interested in this Program? Secure your spot now!
Upcoming Batches
Interested in this Program? Secure your spot now!
What People Say About Us
Himanshu Tyagi
I have completed the course in 3-4 months of DIGITAL MARKETING training under the guidance of Experts Trainers. It was the best experience to learn under them and their teaching methods are out of the box. Best institute for professional courses and a great place. and very cooperative company with helpful staff.
Related Courses